MySQL database had become one of the go-to inexpensive options for companies looking for relational database around the globe. But with the growing variety and volume of data, new non-relational databases like MongoDB have arisen to attend to the enterprise’s needs of fluid data.
This new class of non-relational database has brought with itself a stiff competition between the two – a newbie vs a veteran: MongoDB vs MySQL.
In a situation like this, it has become all the more difficult for the entrepreneur to choose one database over another, for, at the end of the day, both come with their fair share of benefits.
In this article, we are going to help entrepreneurs understand how the two models stack up against each other and the situations where one emerges better than the other.
Without further delay, let us get started by first looking into the brands that are supporting them individually by basing their database needs on both of them individually.

Although this must have given you a very basic idea of where you should be headed in the choice of the database model when planning your mobile app backend development, let us make it all the more clear.
Here’s a table of difference highlighting what separates the two databases from each other.
MongoDB vs MySQL: Which is Better
[table id=24 /]
While these are the primary point of differences, the list does not end here. Let us look at other difference points that stand between MongoDB and MySQL.
A. MySQL vs MongoDB: Database Structure
MySQL database structure stores the data values in tables and makes use of the SQL to access them. It uses schema for defining database structure. The schemas require that the rows inside the table have the same structures, with the values also been represented by specific data types.
In the MongoDB database, data gets stored in the JSON-like documents which come with varied structures. In order to better the query speed, it stores related data sets together which are then accessed with the help of MongoDB query language.
The database is schema-free, meaning it allows the mobile app developers to create documents without the need to defining the document structures.
B. MySQL vs MongoDB : Index Optimization
Both MongoDB and MySQL use indexes for finding data quickly. The difference in approach, however, comes when an index is not found or defined.
In the case of MySQL index optimization, when the index has not been defined, database engines are made to scan the complete table for finding relevant rows.
In MongoDB, when an index cannot be found, every single document inside a collection should be scanned for selecting the document that offers a match to query statement.
C. MongoDB vs MySQL: Database Deployment
MySQL is written in C++ and C language and contains binaries for following set of systems: OS X, Microsoft Windows, AIX, Linux, FreeBSD, BSDi, IRIX, HP-UX, NetBSD, etc. Let’s look at MongoDB database deployment was also written in C++, C in addition to JavaScript and contains binaries for following systems: OS X, Linux, Windows, and Solaris.
D. MongoDB vs MySQL: Type of Clustering or Replication
MySQL database supports the master-master replication and master-slave replication. This multi-source replication enables you to replicate from multiple masters in parallel.
MongoDB, on the other hand, supports a built-in replication, auto-elections, and sharding. Using the auto-elections, developers can set a secondary database for automatically taking over when the primary database fails. Sharding, on the other side, allows horizontal scaling – something which is very difficult to implement with MySQL.
E. MongoDB vs MySQL: The Offerings
MySQL offers an Oracle Lifetime Support at three primary levels:
- Premier for versions 1 – 5 years old
- Extended for versions 6 – 8 years old
- Sustain for versions 9+ years old.
Every one of the levels offers 24×7 tech support with access to complete knowledge base, bug fixes, maintenance releases, updates, and patches.
MongoDB provides an Enterprise-Grade Support which extends beyond the break/fix model. It gives you round the clock support in addition to an extended lifecycle support add-on, which gives the flexibility to upgrade to a newer version at own pace.
F. MongoDB vs MySQL: Developer Productivity
When we talk about the MongoDB vs MySQL performance point, the point falls in the kitty of MongoDB.
Creating applications using MySQL is much slower for it makes use of a very rigid table structure model.
By working with data which are flexible as the JSON documents, MongoDB accelerates the development cycle by around 4 to 5 times. It documents the map naturally to the object-oriented programming languages, making it easy for developers to visualize how the application data is mapped to data in the database.
G. MongoDB vs MySQL: Speed
In the MySQL database, the data gets spread across various tables, meaning multiple tables have to be accessed for reading and writing the data. This lowers the application speed to some extent.
One of the MongoDB advantages is that the data for an entity gets stored on a single document. This makes the applications faster. It also brings the facility to write and read data all in one place.
H. MongoDB vs MySQL: Atomic Transactions
MySQL database supports the atomic transactions, meaning you can have multiple operations inside a transaction.
MongoDB with its 4.0 version also added the support for multi-document transactions. This move made it a powerful open-source database in an unstructured space. While there are still some limitations in terms of unsupportable operations, the database is still a major boon for the developer community.
I. MongoDB vs MySQL: Distributed System
MySQL has not been built on any distributed system architecture,‘MySQL Cluster’, however, is the new distributed database addition in the MySQL offerings.
MongoDB, on the other hand, is developed entirely on the distributed architecture. Meaning, it offers data localization with the help of automatic sharding and the replica sets for maintaining an ‘always-on’ availability. This makes it possible to make the data available globally while being placed locally for low latency access and governance.
J. MongoDB vs MySQL: Native Language Drivers
Even though MySQL comes packages with a JSON support, the developers are still limited to various SQL functionality layers for interacting with the JSON data. For a developer who wishes to interact via APIs which are idiomatic to the programming languages, the layers become an overhead.
With the differences now attended to, we have now arrived at a point where we will be giving you a precise answer to the prevalent question: When to use which database model?
Let’s find out.
Which Database Would Best Suit Your Business Need?
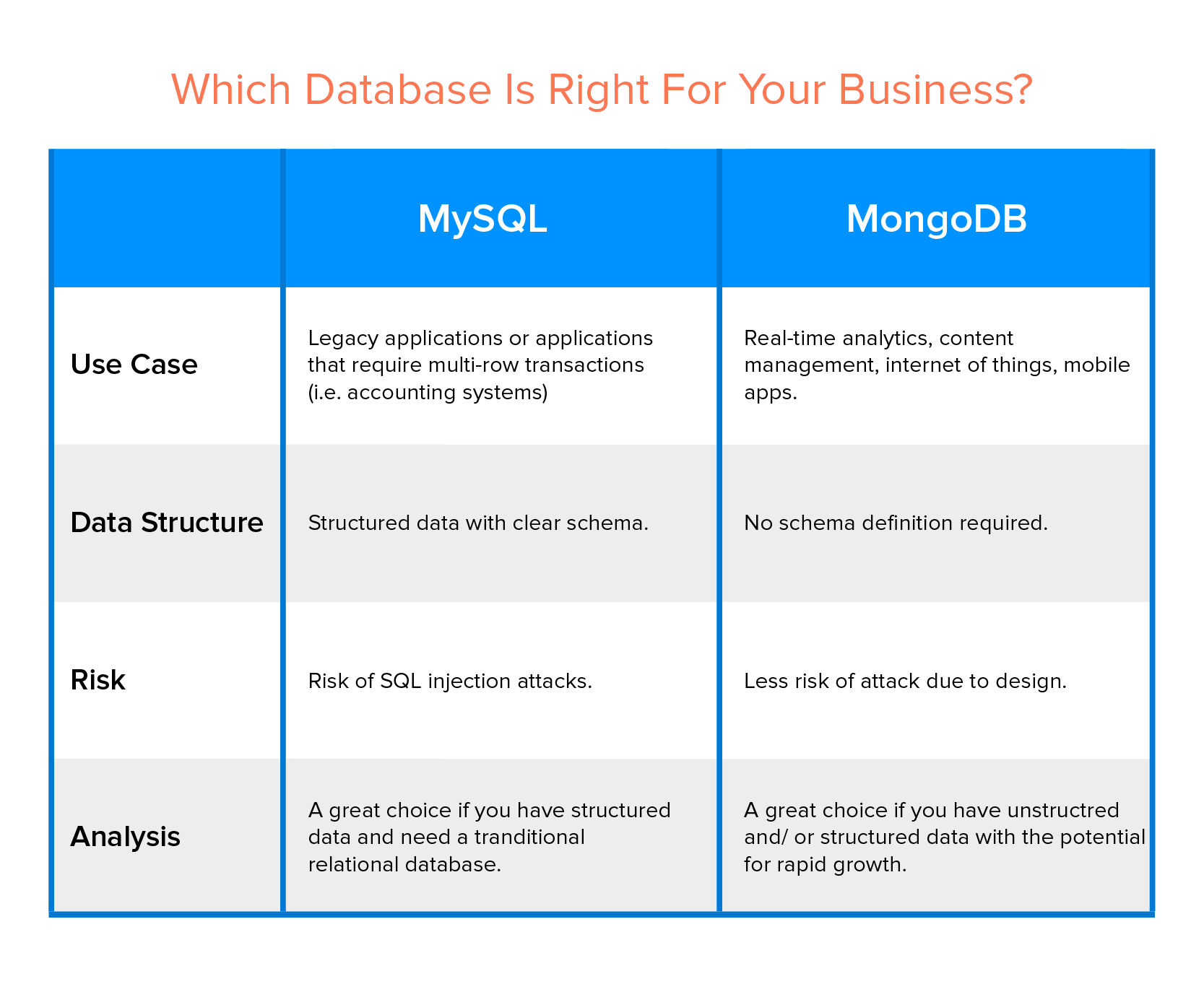
The table above although gives a crisp idea of when to choose which when you are comparing the two databases: MongoDB vs MySQL’s performance points, let us nonetheless break it down for you in much simpler words.
When to Choose MongoDB
- When you require high data availability in addition to a fast, automatic, and instant data recovery.
- In case you work with an unstable schema and would want to lower the schema migration cost.
- If your services are mostly cloud-based, the native scale-out architecture that MongoDB comes with will be suitable for your business. For the architecture is enabled by sharding, which aligns with the agility and horizontal scaling offered through cloud computing.
When to Choose MySQL
- In case you are only starting your business and the database is not going to scale much.
- If you have a fixed schema and a data structure which won’t change over time.
- If you are looking for high-performance ability on a low budget.
- If your requirement would be a high transaction rate
- If the security of the data is your foremost priority (MySQL is a lot more secure than any DBMS).
With this, we have now looked into everything that is needed to get you at a position where you are able to decide which database would be better than the other. But if you still have some unclarity surrounding you, get in touch with our team of Database consultants today.
FAQs About MongoDB vs MySQL
Can MongoDB replace MySQL?
MySQL comes with a different set of advantages compared to MongoDB, so it won’t be possible to comment with surety that MySQL will be replaced by MongoDB program.
What are the advantages of MongoDB?
There are a number of benefits that come associated with MongoDB database:
- It is schema-less
- The clarity in a single object structure
- Deep query ability
- Tuning
- Ease of scaling
What type of database is MongoDB?
MongoDB is a non-relational database.
When to use MongoDB in place of MySQL?
Here are the instances where using MongoDB makes more sense:
- When you need higher data availability
- When you want to lower the schema migration cost
- If your services are mostly cloud-based.

strategies your digital product.




