Every time a new version of Android comes out, it is mostly a very big deal. In every new version, there are a bunch of new features, a set of design changes, and most of the times, a stream of phones to go along to suit the new version.
And when the launch is something as major as a slimmed down version of Android, the event is bound to make some noise.
Google, in I/O 2017 announced the launch of an OS that would run on low-cost smartphones that predominantly dominate the developing nations and it took a year for OEMs to launch their Android Go Devices.
Among the other MWC announcements, one was the names of devices that would have Android Go.
Here are the Android Go devices – Alcatel 1X, Nokia 1, LavaZ50, ASUS Zenfone Live L1, and Huawei Y3 etc.
Android Go – The Idea Behind Android’s Slimmed Down Version
Let us start with the basic question first. What is Android Go?
Android Go is a slimmed down version of Android, which is designed specifically to run on the entry-level phones. The business strategy that runs behind Android Go is to expand the business to the developing nations, which on one hand has the advantage of the high user base, but on the other hand, face restriction from low storage space, high app size, and low RAM size.
To solve these three primal issues that keep Google from making Android reach its market potential, the brand launched Android Go that –
- Make the Android run on the phone with 1GB RAM or even less
- Make the OS takes lesser space
- Make the preinstalled apps take lesser data and space
In order to serve the developing nations to their best intent, the tech giant has brought about three major changes in its ecosystem – Operating System. Play Store. Apps.
Let us look at all three of the structural changes that Google has brought with Android Go, one at a time.
Operating System
The operating system of Android Go has been based on Oreo, but has been optimized for running on smartphones with over 512 MB to 1 GB RAM. Size wise, it takes half the space of Android Nougat, allowing devices with less storage a space to hold number of apps and media out of the box.
Devices that run Android Go are known to open the apps 15% faster than the other Android software. In addition to that, Android Go users get ‘data saver’ feature in default mode, which helps them consume lesser mobile data.
Apps
Like the new OS, Google has developed new apps as well to help make better use of the device’s memory. These apps require around 50% lesser space and tend to perform a lot better in the low end hardware.
Android Go devices come with these pre-installed apps –
- Google Assistant Go
- Google Go
- YouTube Go
- Gmail Go
- Google Maps Go
- Gboard Go
- Chrome
- Google Play Store
- Files Go
While these apps are a lot faster and smaller in size, they come with some features missing. Now although the Android Go apps are restricted in number, as of now, the number if expected to increase in the coming future.
[Fact: All the pre-installed Android Go apps are PWAs. And this is what Google wants you to know about PWAs]
Play Store
To help keep the lightweight experience in sync throughout, Google has launched an all now Play Store as well.
Android Go Play Store provides the same content as your regular Play Store, just with a storefront that is suited for the low-storage devices. The store has a featured section which recommends users the apps that are designed and developed specifically for their Android Go smartphones.
While most of these changes are in the background, let us look at the changes that are visibly present between Android Go vs Regular Android.
Visible Differences in Android Go vs Regular Android
1.Recent Apps
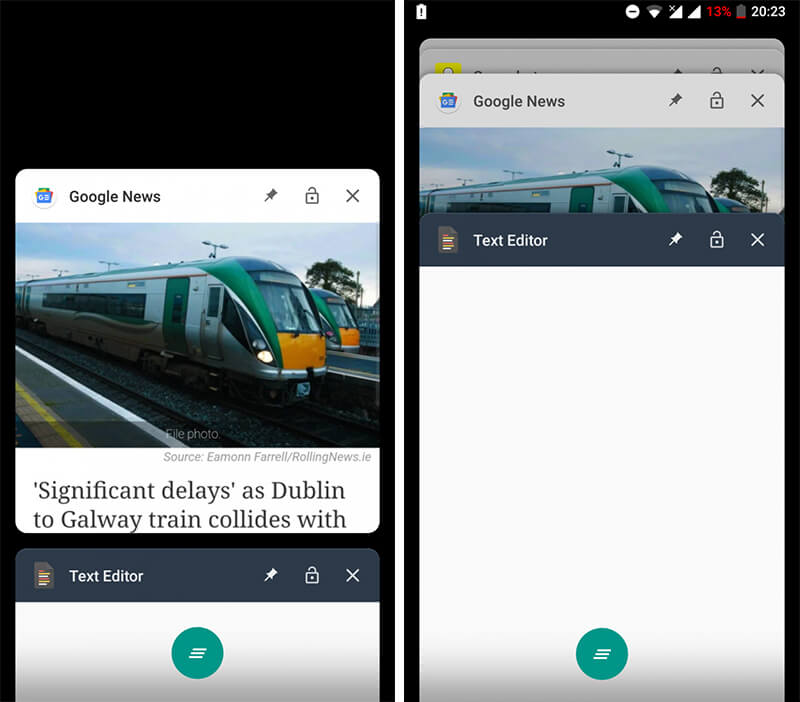
*Android Go on the Left and Regular Android on the Right
The thumbnail of recent apps in Android Go is lot smaller than the one in your regular Google application. It expands to fill the device screen as the app loads, giving the impression that the apps are loading much faster.
2.Gmail
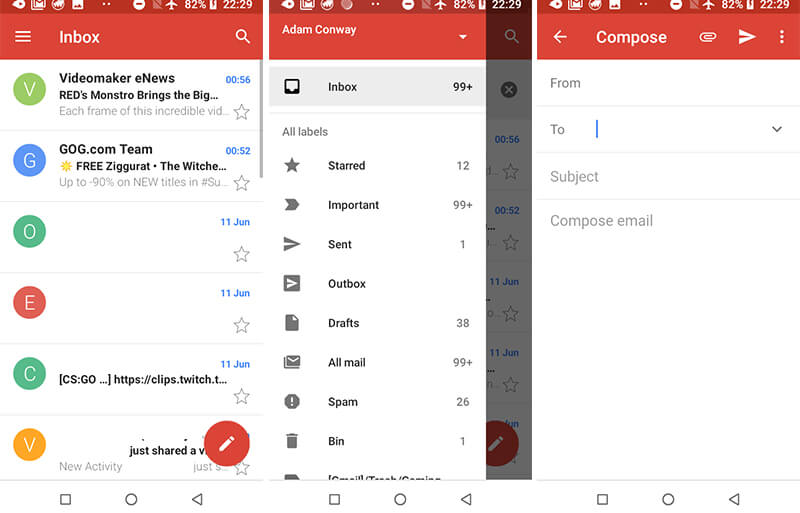
*Gmail Go
With Gmail Android Go Application, Google has cut back on graphics to a great extent. While visually, there are not a number of evident changes, performance wise, Gmail Go make use of a webview that makes the performance choppy.
3.YouTube
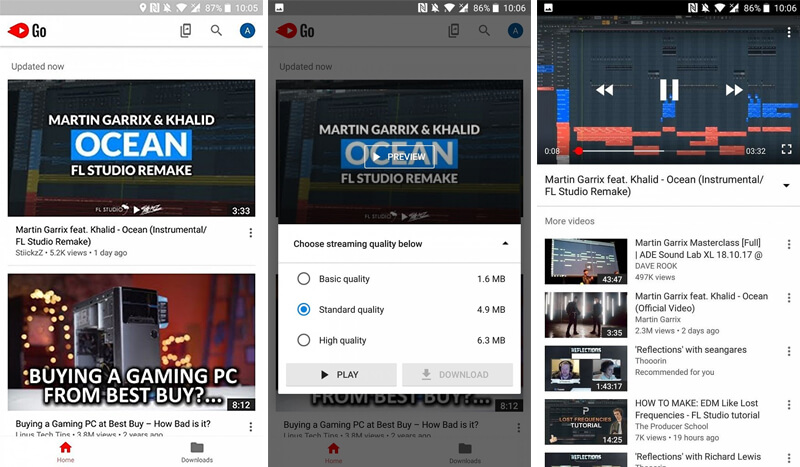
As compared to the regular YouTube, YouTube Go is a lot simpler and has much less functionality. While UI wise, again, there is not a stark difference, but there are evidential changes in terms of functionality in case of YouTube Go – The amount of data a video will consume is clearly specified, there are no likes/dislikes and comments option anymore.
4.Google
Google Android Go Application has a lot more to offer than your regular Google application. There are a number of customization options as well as the ‘Trending Search’ option, which was earlier missing in Google. The only thing missing in Google Go are the recommended cards.
As for the Assistant Go, while it is not completely different from Google Assistant, there are a few restrictions – there is no configuration option, the assistant doesn’t set default players, and it cannot control the hardware of the phone.
5.Google Maps
The resemblance between Google Maps and Google Maps Android Go Application is uncanny, Maps Go is a case of perfect recreation when we talk about visuality.
Functionality wise, there are some obvious limitations, which might be a deal breaker for a number of users. The real-time turn-by-turn navigation is entirely missing in Google Maps Go, also reviews are missing in Google Maps Go.
With all these functionalities and structural changes, the aim that Google is looking to fulfill with Android Go is to improve the overall user experience of the entry-level smartphone user base. While Google has done a lot in terms of optimizing their experience, it comes on us, Android app development companies to take the journey further while expanding our business beyond geographies.
With that respect, here is the answer to How to get Android Go in your Android App suite.
Steps to Optimize your Android App Development Process to fit in Android Go a.k. How to Develop Android Go App
The process of converting your regular Google application into Android Go application would start with the answer to your app strategy.
When it comes to developing an app that is optimized for devices that are designed according to the Android Go standards, there are three options that you can choose from –

Have a Common App
Use same app for all – Android and Android Go devices offering identical experiences. The android app here should be multi-binary, but shouldn’t have any particular experience for the less RAM devices. You can use Android App Bundle for this to save upto 65% in size without refactoring the app code.
Have one App with Different APKs
Use same app for Go devices and other devices, with different set of experiences. For this, you will have to develop different APKs, with one targeting the new android.hardware.ram.low dimension and other APK focusing on other devices.
Have Two Apps
Develop a Lite app targeting on the Android Go devices and keep your other Android app as it is.
[Know all about Lite Apps Trend]
Once you have decided on the app development strategy you will be following, look at these key considerations –

Ensure App functions without Crashes and ANRs
Application not responding and high crash rates are the two factors that negatively impact user retention rate. Make use of tools like Crashlytics and Android vitals to check the crash free sessions and ANR rate of your Android app.
Focus on Android Oreo
Android Oreo comes with a number of resource optimization like the Background Execution Limit that ensure proper running of processes in the background. Read through the Google Play migration guide in case your app is not targeting API 26 or more.
Keep the App Installed Size Low
Since the Android Go apps will be focusing on low MB, entry level smartphones, you will have to ensure that your app is under 40 MB. To achieve this, either optimize your present APK or create a different APK targeting the Go users.
Here are a few tips on how to lower the app size –
- Use Android App Bundle
- Replace the JPEG/PNG files with the WebP assets
- Replace raw audio format with AAC or MP3
- Make sure that the libraries are updated
Keep Memory Footprint Low
When you test the APK, look at the PSS to analyze the amount of memory the app takes to start on the device.
Keep Cold Start Time Under 5 Seconds
As you run the test for the cold startup time after completing a full reboot of the test device, ensure that the app becomes interactive within 5 seconds of being launched on the users’ device.
So here was all that you need to know about Android Go, Android Go vs Regular Android, and finally how to develop an app for Android Go. Now that you have all the necessary information, what are you waiting for? Contact a team of Android Go experts and expand your business.

strategies your digital product.




