Debit and credit cards have become the norm in no-cash transactions to pay the merchants because of the commonality in their worldwide standards and ubiquitous acceptance. While debit and credit cards have taken the position in merchant transactions, there is no easy standard when making payments on a peer to peer level. This lack of a set standard is definitely not because of the lack of Peer to Peer transactions’ need.
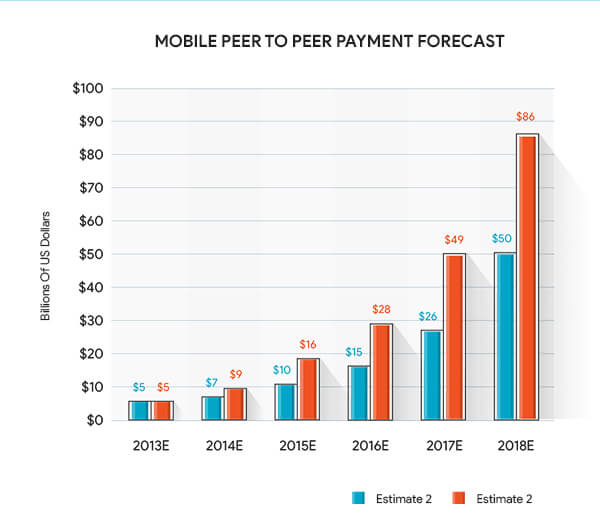
Needs like splitting the rent and utility bills, diner bill sharing, monetary birthday gifts, and splitting vacation’s bills are the highest use cases of P2P payments and globally that represents over $50 – $80 billion in yearly payments.
The market demand for mechanisms that would lower the ATM visits and restrict the transfer of large amounts between two people has given birth to vendors who have stepped up to give the solution to ease the P2P Payment transactions. This surging demand has directly brought about a growth in peer to peer payments market size.
What is peer to peer payments?
Peer to Peer Payments or P2P Payments is an electronic transfer made by one individual to another with the help of mechanism that is called P2P Payment Application. Through these applications, every individual account gets linked to the other user’s digital wallet. As soon as the transaction occurs, the account balance in application records it and pulls money directly from one user’s bank account or app wallet and send it to other’s.
P2P Payment Apps can be divided into three categories and each of the categories have their own set of market leaders.
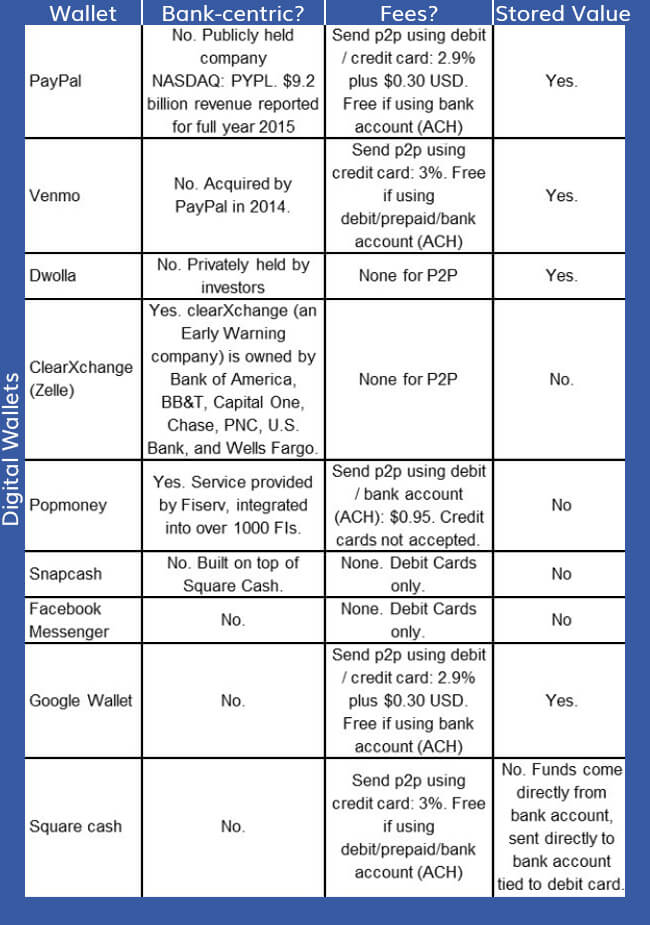
1. Standalone Services (PayPal and Venmo)
These P2P vendors do not rely on banks. They have their own mechanism of storing and dealing with money, without any link to any financial institution. They all have the Wallet feature which makes it possible for users to store money before offloading in some bank account or sending it over to their peers. PayPal user base, since its inception, has grown to 202 countries where around 188 million users transact funds in more than 25 currencies. While PayPal continues to maintain its position for being the largest P2P Payment service provider, Venmo is the one that is fastest growing, in terms of transaction, the platform saw 140% rise in transaction from 2015 to 2016 alone.
2. Bank Centric (Dwolla, Zelle, and Popmoney)
There are some P2P Payment apps that involve bank as one of the parties when doing transactions. While most of the banking institutions have their own apps, there are peer to peer payment apps that facilitate the fund transfer through its partner bank and credit unions. ClearXchange, who owns Zelle is developed by the top US banking institutions like BB&T, Chase, U.S. Bank, Wells Fargo, and Bank of America, making it one of the safest platforms, matching the safety standards of that of a banking establishment.These apps draw from and deposit directly into bank accounts instead of a stored currency account.
3. Social Media Centric (Facebook Messenger, SnapCash, Google Wallet)
The underlying device in both Peer to Peer Payment Apps and the Social Media platforms is same – Mobile. It was about time that Social Media giants entered the mobile P2P market. In 2015, Facebook launched its Messenger Payment feature allowing people to transfer money using their debit or credit cards, without leaving messenger. SnapCash was developed some four months before Facebook added the payment option in messenger. The app is built on top of the SquareCash, the product of Square. Backed by the security history of Square, payments made through SnapCash are at par with the PCI DSS standard maintained by Square.In 2015, Google acquired Softcard, the mobile wallet offered by US biggest carriers – Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile. The name Google Wallet was changed to Android Pay on these device. The definition of Google Wallet nametag was now restricted to P2P Payment service that included store value account that could be accessed through an app other than Android Pay, linked plastic cards, and Gmail.
Common Underlying Features in every successful P2P Payment Apps
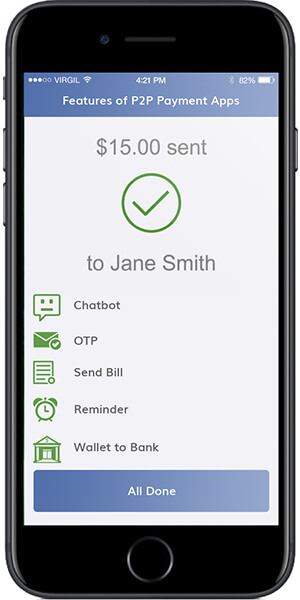
There are some features that we, as a mobile app development company incorporate in every single of our P2P Payments apps that we have developed. These are the ones that you should have in the apps that you are all set to offer to the flourishing Fintech world.
- Unique ID/ OTP
Every Fintech app has an OTP or unique id that is sent to and verified by the sender before the money is deducted from his/her account or wallet. To make apps even more secure, some P2P Payment Service Providers even ask for the OTP every time one opens the app.
Technical Frameworks used – Third party SDKs like: Twilio, Firebase, Nexmo, Digimiles
- Notification
There is a feature in the app that allows people to inform when the payment has been initiated and when it has been received. Using this, users are notified of any of their account or wallet activity. For apps that have extended their services from just peer to peer transactions to individual transactions like bill payment, ticket booking, etc. this can be used to notify the users of the upcoming bill due dates.
Technical Frameworks used – Rest APIs, Chrome notifications, Amazon SNS, Firebase cloud messaging, and APNS.
- Send Bill, Invoice
There should be a feature to scan and send the bill to the person who needs to make the payment. Along with that, both the parties: Sender and Receiver should be able to receive a generated invoice of the transaction, which should be saved in the app itself.
Technical Frameworks used – Rest APIs, Bamboo invoice
- Transaction History
Every P2P Payment app should have the feature of Transaction History that would give the users the summary of all their past money transactions made through the app.
Technical Frameworks used – Rest APIs
- Chatbot
There are various points of disputes that can come up when transacting funds through an app, from a lost internet connection in the middle of the transaction to the wrong deduction of amount from the wallet or account. It is imperative that the user is able to report the incidents on time, this is where Chatbots feature comes into the picture.
Technical Frameworks used – Third Party party SDKs – Zendesk, Microsoft Bot Framework, LUIS, Wit.ai, Api.ai, Chatfuel, Facebook Messenger Chatbot, and Amazon Lex
- Transfer Amount to Bank
Generally, users look for a way to transfer the amount that they receive through the apps to their bank accounts. While every app has its own set of business model, this is one of the most preferred features of the P2P Payment industry.
Technical Frameworks used – ACH, Dwolla
This is about the features that should be added in the apps. But along with the must haves, there are scenarios that should be avoided as well. While most of them are not in your hands, there are some technical issues that you can easily overcome by being cautious.
Let’s look at a few of them –
Challenges that Peer to Peer Payment Apps should be prepared for
Even though the world is now moving towards the digital money era, there are some challenges that the industry that persists and should be overcome for a P2P Payment App to survive in the market. Let us look at both technical and non-technical challenges that are still staring at the P2P Payment industry –
Starting with Non – Technical first
Regional Limitations
The major players of the P2P industry are restricted in their geographical limitations. It is still not common for a service provider to enable fund transfer between two nations. As the Fintech industry continues getting overcrowded, it is very important for a brand to expand their geographical reach in order to come out as an industry leader.
1. Lack of Open Loop Solutions
Presently. When making payments through P2P Apps, both the parties – one making the payment the other receiving it, should be on the same platform. While it easier when we are transferring funds between people we know, there are times when we take or conduct one time payments with people we don’t know. The open loop platform enables the users to conveniently accept and transfer funds from/to anyone – eliminating the need for the involved parties to be connected through one platform or give-and-take personal information.
2. The cases of dispute
There are a number of disputes’ points that are associated with P2P Payment Apps. Suppose you initiate payment to someone and instead of going to him/her it goes to someone else or what would you do when an amount is debited from your wallet or account but the person it was supposed to reach, haven’t received it. Like these, there are a number of things that can go wrong within the minutes of money leaving your wallet and reaching somebody else’s account. It is important that as a P2P payment app developer, you keep a note of these issues.
3. Slow changing Mindset
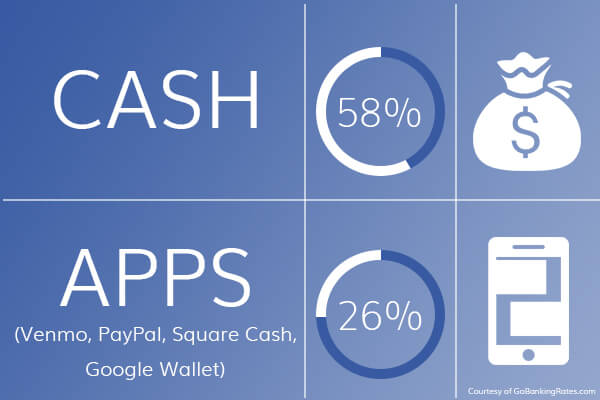
While people are adapting the mobile peer to peer payment options, the industry is still growing at a slightly slow speed. People are still more comfortable in using cash and card instead of mobile apps and the reason behind this is not the UI or accidental lagging, the reason is being unsure of the safety measures these apps follow to save the confidential information.
{Read Also: Mobile Application Development Guide: Everything Worth Knowing}
While these were the non-technical issues hovering around the industry, let us now look at the technical challenges they are facing –
1. Security
One of the biggest challenge that all P2P Payment Service Provider faces is security. Going by the track record, hackers have been able to get into some of the most secured institutions and platforms like NIC Asia Bank and PayPal. The high level of vulnerability has made Security one of the biggest challenge in the Mobile P2P Payment industry.With the huge number of confidential data being stored in one place, it is imperative for the P2P Payment service providers to create a secured data record management system.
2. Comply with PCI DSS It is imperative for every brand dealing with confidential banking information to follow the PCI DSS Compliances. To be eligible for the certificate, the P2P Payment service providers should meet these criteria –
- Develop and Maintain secure system and network
- Have a vulnerability management system in place
- Create strong access control standards
- Safeguard confidential information
- Continuously test and monitor networks
- Maintain and update all information security policy
3. Currency Conversion

Another challenge that the P2P Payment Service providers face is calculating and converting currencies in real time. With 180 currencies across the world, it can get difficult for the service providers to create a mechanism that keeps everything on track.
Along with this, the money conversion and fund transfer needs to be done in the smallest time possible: an event which is easier when banking institutions are involved, but a little complex when it comes to a digitized market.
What’s the next level?
There are continuous symptoms of growth for blockchain and cryptocurrency use inside the mobile payments industry. The working behind bitcoin has even become one of the most talked about topics in the current times. Companies like Movile have already realized the scope of using bitcoin within in-game micro purchases. Bitcoin has even become an alternate mobile payment coinage in some developing economies such as Brazil.
Let us look at what the Blockchain and Cryptocurrency is all about –
Blockchain Technology
The Blockchain is an unsigned online ledger, which makes use of data structure to ease our transaction processes. It allows its users to edit the ledger securely without involving a third party.
While bank’s ledger is linked with a centralized network, Blockchain is completely anonymous thus protecting its users’ identities. This anonymity makes the technology a secure way to do transactions.Blockchain is always implemented on distributed networks. The algorithm that it uses lowers the dependency on people to authenticate the transactions, giving Blockchain the potential to unsettle the prevalent financial systems.
The electronic record of transactions is incessantly maintained and then verified in the ‘blocks’ of records. Finally, the meddle-proof ledger is then shared between the parties on their computer servers by taking help of cryptography.
Blockchain is expected to lower down the inefficiencies and costs involved in dealing with the financial sector.
Cryptocurrency

Cryptocurrency is a digital currency that exists and operates in digital peer to peer networks. It is not a string of data like your regular MP3 and Video files that can be copied. Cryptocurrency is actually an entry on a global ledger known as Blockchain.
How does it work?
When you are sending someone cryptocurrencies, you are not sending them a series of files. Instead, you are writing down the exchange in the ledger, a.k.a. Blockchain. Now even though Blockchain is a decentralized record, there’s no group of people who update the ledger, like what happens in banks. The mechanism is completely decentralized.
There are people who volunteer to keep the tracks of transactions and continuously maintain them in ‘Blocks’. So now when you want to transact currency, you will have to announce it to the table so that people who are maintaining the ledgers can update them.
Fintech along with its continuous advancements is all set to make Peer to Peer Payment much stronger and easier to adopt, giving a push to companies to get involved in the industry with their own applications.
Are you ready for the move?

strategies your digital product.





