Every year, Android keeps coming up with a new version, which is a much upgraded version of its previous self. The transformations, which are sometimes as drastic as a new look and feel of the device or at times are just a bundle of security patches. But, however big or small they are, Google continues to offer something new for both the users and developers to experience.
The number of updates are so many that is extremely difficult to keep up with them. As a developer who has received a query on which version to go with for a new android app or simply as an android enthusiast, it is a tad difficult to keep up with what’s new and what faded over the versions.
Through this article, we aim to keep you updated. Read this as a quick comparison sheet that has the information of what changed over time.
Here is a comparison of three of the Android’s operating system which are present on maximum of the Android devices, currently.
But before we start with seeing the factors that separate them from one another, here is a summary of theirs –
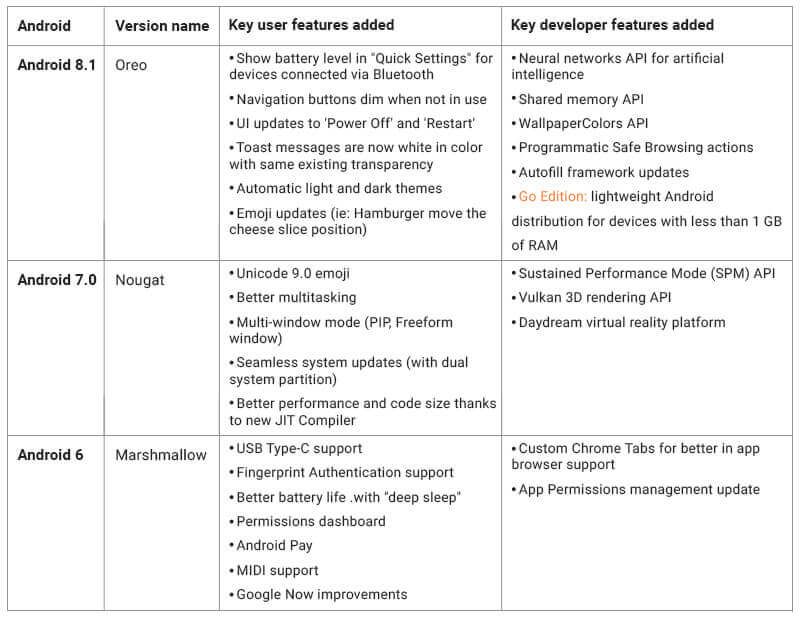
Oreo
The latest entrant in the Android market, Oreo has been introduced with a set of revolutionary changes. From the new PIP mode to notification dots, and a whole new level of security blanket, Oreo has set a whole new set of examples in the history of Android updates.
Nougat
With elements like multi-window view, quick switch between apps, and a whole new notification bar, Nougat has brought with itself over 1500 emojis and a battery saver function that doesn’t wait for device inactivity to start working.
Marshmallow
The version brought with itself Doze – Android’s most powerful battery saver mode, till date. Marshmallow also saw permissions, which can be switched on and off as per users’ needs. One of the biggest changes that this version came with, was the Fingerprint scan, which allowed users to unlock their devices just with their fingertip scan.
Now that we know what the versions came with, let us begin with the comparison of the three updates.
Android Oreo vs Android Nougat
Here’s a list of differentiating factors between the two versions of this OS, presently available on 28% Nougat and 1.1% Oreo devices.
Battery Life – Oreo vs Nougat
While Nougat uses the Doze on the Go feature that puts the device on sleep mode after a fixed time of inactivity, to save battery life, Android Oreo uses Doze on the Go along with a few other strategies to save the battery life.
Oreo kills apps running in the background after minutes of inactivity. Also it limits location reading power of apps that are running in the background – both the strategies together help extend the battery life even further of users who have upgraded to Oreo.
However, Nougat is also not lagging behind when it comes to battery life.
Quick Settings – Nougat vs Oreo
One of the most noticeable changes in Oreo, when compared to the Nougat version has been the Quick Settings bar. While Android Nougat has both – a dark and light gray mixpanel for the device’s Quick Settings section, Oreo has changed it and has made it completely white, a visible difference from Nougat’s mute grey.
{Read Also: Mobile Application Development Guide: Everything Worth Knowing}
Notifications – Oreo vs Nougat
In Nougat, once you disable the notifications of an app for any specific activity, it blocks all the notifications that comes from that specific app. This means that none of the critical notifications will ever come through.
However, in Oreo, users can disable the specific activity’s notifications in an app so that while the users are not getting spammed but they are not missing out on critical notifications too.
App Interaction – Nougat vs Oreo
Notification Dots is the new element introduced by Android Oreo, which has made it much easier to take action against an app. By pressing on the app for long, you get an option called ‘App Info’ which open up to a screen that has information about the app, and has the option to uninstall and force stop the app.
In Nougat, you can still interact a lot with the app without opening it specifically. Example, you can reply to a Hangouts message straight from the home screen notification bar, only the Oreo’s App Info is missing in Nougat.
Installing Applications from the External Sources – Nougat vs Oreo
With Oreo, has aggravated the security when we talk about downloading the apps and giving them a free hand. Oreo allows you to individually deny or grant permission to every App.
In Nougat, all users have to do is give a one time access to the device to install apps from the external sources, unlike Oreo where users have to manually give permission to every app.
Improvements to the Android Runtime – Nougat vs Oreo
With Oreo, the operating system giant has made the app loading and a runtime, which is two times faster than what is seen in Nougat.
Animations like swiping down of the bar reveal the notification message have also been tightened which gives the illusion of speed in Oreo. But, otherwise, there are not many differences in other elements like when users switch between different mobile applications.
Android Nougat vs Android Marshmallow
Here’s a list of differentiating factors between the two operating system versions, presently available on 26% Nougat Devices and 28% Marshmallow devices.
Battery Life – Nougat vs Marshmallow
Doze – the powerful battery saving feature was introduced at the time of Marshmallow, but it only became better with Nougat.
In Marshmallow, the power saver mode only gets activated after a prolonged period of inactivity but in Nougat, the second you lock your phone screen, it goes into sleep mode, which seem to have brought a great deal of battery juice for the Nougat users.
Notification Interaction – Marshmallow vs Nougat
Nothing much happened on the Notification front with Marshmallow. But, Nougat revamped the notification bar 180 degrees.
With Nougat, the users can now directly send replies from their device’s home screen, along with viewing notification bundled up individually app wise. Something which is not possible in Marshmallow.
Closing of Apps – Nougat vs Marshmallow
In Marshmallow, users would have to close all the apps individually in the recent/running app stack. But, with Nougat, Google enabled to close all the running/ recent apps with a single click.
Data Saving – Marshmallow vs Nougat
Nougat brought a revolutionary change in users’ data saving capability. In Marshmallow, users are dependent on third party VPNs to limit the data usage of an app, but with Nougat, things are different.
In Nougat, users can view all the apps that are sucking up their data in their device’s settings tab and then control the data by force stopping the app from there itself.
Hope this article helped you with knowing how the three most used Android version separates from other.
Think we missed a factor? Feel free to add it in the comments below.

strategies your digital product.





